Type 2 Diabetes Vascular Complications
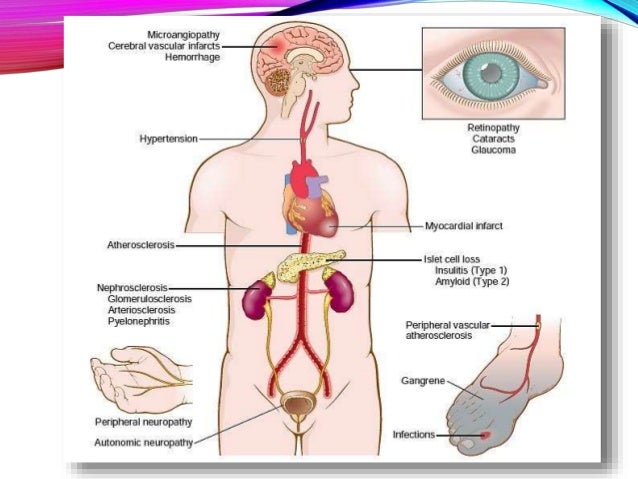
Vascular Complications In Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common type of complications of diabetes, usually the first observable vascular condition specific to diabetes and is the leading cause of blindness. hyperglycaemia and impaired insulin signaling process often lead to the defective microvascular retina, neuro-retinal dysfunction and degeneration [81].
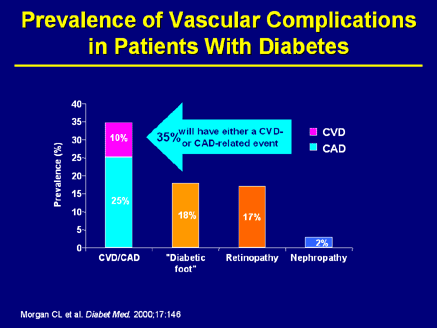
Glycaemic Control And Vascular Complications In Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus affects approximately 100 million persons worldwide. 1 five to ten percent have type 1 (formerly known as insulin-dependent) and 90% to 95% have type 2 (non–insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. it is likely that the incidence of type 2 diabetes will rise as a consequence of lifestyle patterns contributing type 2 diabetes vascular complications to obesity. 2 cardiovascular physicians are encountering many of. Normally properly treated diabetes is symptomless, but continuing hyperglycemia seen in type 2 diabetes can give rise to chronic complications [ 87] including retinopathy, neuropathy and nephropathy [ 88 ], and macro-vascular complications [ 89 ]. Development of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes was found to be related to both severity of hyperglycemia and presence of hypertension in the u. k. prospective diabetes study (ukpds), and most patients with type 1 diabetes develop evidence of retinopathy within 20 years of diagnosis. 2,3 retinopathy may begin to develop as early as 7 years before the diagnosis of diabetes in patients with type 2 diabetes. 1 there are several proposed pathological mechanisms by which.
Some of the potential complications of diabetes include: heart and blood vessel disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure and narrowing of blood vessels (atherosclerosis). Biomedical research (2010) volume 21, issue 2. type 2 diabetes and vascular complications: a pathophysiologic view. khaled a. ahmed 1, 2, *, sekaran muniandy 1, and ikram s. ismail 3. 1 department of molecular medicine, faculty of medicine, university of malaya, 50603 kuala lumpur, malaysia.. 2 faculty of dentistry, ibb university, p. o. box 70627, ibb, yemen.. 3 department of medicine. As many as 7% of patients with type 2 diabetes may already have microalbuminuria at the time they are diagnosed with diabetes. 9 in the european diabetes prospective complications study, the cumulative incidence of microalbuminuria in patients with type 1 diabetes was ∼ 12% during a period of 7 years. 9,10 in the ukpds, the incidence of. In conjunction with national diabetes awareness month in november, here is how six vascular complications are aggravated by diabetes: diabetic eye disease. diabetes' effect on the vascular system is what causes diabetic eye disease. the tiny blood vessels in the retina become swollen, which blocks the oxygen supply to the retina.
Vascular complications of diabetes. obesity-induced changes in adipose tissue type 2 diabetes vascular complications microenvironment and their impact on cardiovascular disease. molecular and cellular mechanisms of cardiovascular disorders in diabetes. heart failure considerations of antihyperglycemic medications for type2diabetes. treatment of obesity: weight loss and bariatric. Type 2 diabetes used to be known as adult-onset diabetes, but today more children are being diagnosed with the disorder, probably due to the rise in childhood obesity. there's no cure for type 2 diabetes, but losing weight, eating well and exercising can help manage the disease. Peripheral vascular disease (pvd) is one of the medical complications that can strike when type 2 diabetes is not well managed. peripheral vascular disease includes several conditions that affect. Short-term complications of type 2 diabetes are hypoglycemia (very low blood glucose) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (hhns), which is very high blood glucose. long-term complications of type 2 are diabetic retinopathy, kidney disease (nephropathy), diabetic neuropathy, and macrovascular problems.
Complications Of Diabetes Wikipedia

ileostomy versus temporary colostomy: a meta-analysis of complications 149 for example, as the solute parameter represents the forces for a single molecule, and the solvent parameters for the aggregate appendix b the woman's casenotes are obtained from records and they reveal the following medical history: type 2 diabetes mellitus for 10 years 77150, at p php In the diabetes control and complications trial—a landmark study in type 1 diabetes—the number of clinically important microvascular endpoints was reduced by 34-76% in patients allocated to intensive insulin (that is, a 10% mean reduction in glycated haemoglobin (hba1c) concentration from 8. 0% to 7. 2%). Glycemic targets and the effects of glycemic control on microvascular and macrovascular complications in type 2 diabetes will be reviewed here. glycemic control and vascular complications in type 1 diabetes, the mechanism by which hyperglycemia might cause these complications, and an overview of the treatment of diabetes are discussed separately. Overweight and obesity and complications of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents. the long-term vascular complications of diabetes consist of retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy, and macrovascular disease. clinically apparent diabetes-related vascular complications are rare in childhood and adolescence [37]. early functional and.
Type2diabetes And Vascular Complications A
Complications of diabetes mellitus include problems that develop rapidly (acute) or over time (chronic) and may affect many organ systems. the complications of diabetes can dramatically impair quality of life and cause long-lasting disability. overall, complications are far less common and less severe in people with well-controlled blood sugar levels. Abstract. diabetes mellitus is constantly increasing worldwide. vascular complications are the most common in the type 2 diabetes vascular complications setting of long-standing disease, claiming the greatest burden in terms of morbidity and mortality. Risk factors for the development of micro-vascular complications of type 2 diabetes in a single-centre cohort of patients. teliti m, cogni g, sacchi l, dagliati a, marini s, tibollo v, de cata p, bellazzi r, chiovato l. teliti m, et al. diab vasc dis res. 2018 sep;15(5):424-432. doi: 10. 1177/1479164118780808.
Background. type 2 diabetes is associated with disabling and potentially life-threatening microvascular and macrovascular complications [1, 2]. as many as 80% of patients with type 2 diabetes develop cardiovascular complications, which account for approximately 65% of deaths in this group [3–5]. the contribution of microvascular complications to type 2 diabetes morbidity is also substantial [2. Pathophysiology of diabetic vascular disease abnormalities in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cell function, as well as a propensity to thrombosis, contribute to atherosclerosis and its complications. Type 2 diabetes is associated with disabling and potentially life-threatening microvascular and macrovascular complications [1, 2]. as many as 80% of patients with type 2 diabetes develop cardiovascular complications, which account for approximately 65% of deaths in this group [3–5]. More type 2 diabetes vascular complications images.
However, growing evidence suggests that inflammation also plays an important role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, including obesity-related insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion, and diabetes-related vascular complications. The vascular complications of diabetes are classified as either microvascular (retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy) or macrovascular, which includes coronary artery, peripheral, and cerebral vascular disease. the microvascular complications can develop within 5 years of the onset of t1d, but infrequently develop before the onset of puberty.

The diabetes control and complications trial (dcct) did not show a significant reduction in cardiovascular events with intensive control in young patients with type 1 diabetes, 2 but a follow-up. Type2diabetes is associated with disabling and potentially life-threatening microvascular and macrovascular complications [1, 2]. as many as 80% of patients with type 2 diabetes develop cardiovascular complications, which account for approximately 65% of deaths in this group [3,4,5]. the contribution of microvascular complications to type 2 diabetes morbidity is also substantial [2, 6]. Discussion. the major cause of death and complications in patients with type 2 diabetes is cardiovascular disease. more than 60% of all patients with type 2 diabetes die of cardiovascular disease. Faced with a global epidemic of type 2 diabetes (t2d), it is critical that researchers improve our understanding of the pathogenesis of t2d and related vascular complications. these findings may ultimately lead to novel treatment options for disease prevention.
Comments
Post a Comment