Diabetes Insipidus Vs Csw
Diabetesinsipidus Diagnosis And Treatment Mayo Clinic
Diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus diabetes insipidus vs csw share the first word of their name and some of the same symptoms. but that’s where the similarities end. these two diseases aren’t related. they cause. It can be associated with the syndrome of inappropriate adh secretion (siadh), cerebral salt wasting (csw), treatment of transient/permanent diabetes insipidus (di), and excessive fluid administration in patients with adipsia. these conditions may occur in isolation or may coexist. Diabetes insipidus and diabetes mellitus are two separate conditions and are not related although they share the name “diabetes”. how does the anti-diuretic hormone work? adh is produced in the hypothalamus and secreted/stored by the posterior pituitary gland. Diabetesinsipidus. in diabetesinsipidus, or di, the body releases too less anti-diuretic hormone (adh). it is a disorder of water and salt metabolism marked by extreme thirst and heavy urination. diabetesinsipidus di takes place when the body is unable to regulate the fluids.
Siadh vs cerebral salt wasting syndrome (csws) csws is usually associated with hypovolemia whereas patients with siadh are euvolemic. in addition, patients with siadh exhibit elevated adh levels and rarely develop urine sodium levels > 100 meq/l. patients with csws usually have normal adh levels and often develop urine sodium levels > 100 meq/l. Diabetesinsipidus (di) vs syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (siadh) posted on november 2, 2014 syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (siadh) and diabetes insipidus (di) can confuse anyone because diabetes insipidus vs csw they are both endocrine disorders that involve the antidiuretic hormone (adh).
Siadh Vs Diabetes Insipidus Di Endocrine System Nursing
Diabetesinsipidusvs Siadh Diabetesinsipidus Org
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. since the kidneys don't properly respond to adh in this form of diabetes insipidus, desmopressin won't help. instead, your doctor may prescribe a low-salt diet to help reduce the amount of urine your kidneys make. you'll also need to drink enough water to avoid dehydration. Arieff ai, gabbai r, goldfine id. cerebral salt-wasting syndrome: diagnosis by urine sodium excretion. am j med sci. 2017 oct. 354 (4):350-4. wu x, zhou x, gao l, et al. diagnosis and management of combined central diabetes insipidus and cerebral salt wasting syndrome after traumatic brain injury. world neurosurg. 2016 apr. 88:483-7. Don’t forget to take the siadh vs diabetes insipidus quiz. what is diabetes insipidus and siadh? this is where the body has diabetes insipidus vs csw a problem producing adh (either too much or not enough). what is adh? it is anti-diuretic hormone. this hormone is produced in the hypothalamus, and stored and eventually released in the posterior pituitary gland. Diabetes insipidus (di) vs syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (siadh) posted on november 2, 2014 syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (siadh) and diabetes insipidus (di) can confuse anyone because they are both endocrine disorders that involve the antidiuretic hormone (adh).
Central neurogenic diabetes insipidus (cndi), syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (siadh), and cerebral salt-wasting syndrome (csws) all affect both sodium and water balance; however, they have differences in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Diabetesinsipidus (di) is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. the amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. complications may include dehydration or seizures.. there are four types of di, each with a different set of causes. Background diabetes insipidus. central di3 is caused by a deficiency of antidiuretic hormone (adh), caused by destruction or degeneration of the neurones that originate in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus. hypothalamic tumours (craniopharyngioma and germinoma) represent the commonest causes of di in childhood, followed by langerhans' cell histiocytosis or other.
Diabetesinsipidus Di Vs Syndrome Of Inappropriate
Diabetes Insipidus Diagnosis And Treatment Mayo Clinic
Central neurogenic diabetes insipidus, syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone, and cerebral salt-wasting syndrome are secondary events that affect patients with traumatic brain injury. all 3 syndromes affect both sodium and water balance; however, they have differences in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Diabetes insipidus is a rare disorder that occurs when a person's kidneys pass an abnormally large volume of urine that is insipid—dilute and odorless. in most people, the kidneys pass about 1 to 2 quarts of urine a day. in people with diabetes insipidus, the kidneys can pass 3 to 20 quarts of urine a day. Central neurogenic diabetes insipidus, syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone, and cerebral salt-wasting syndrome are secondary events that affect patients with traumatic brain injury. all 3 syndromes affect both sodium and water balance; however, they have differences in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Cerebral salt-wasting syndrome (csws) is a rare endocrine condition featuring a low blood sodium concentration and dehydration in response to injury (trauma) or the presence of tumors in or surrounding the brain. in this condition, the kidney is functioning normally but excreting excessive sodium. the condition was initially described in 1950. its cause and management remain controversial.
Configctrl2. info. metadescription. Komplikasi diabetes insipidus. komplikasi yang bisa terjadi akibat diabetes insipidus, antara lain gangguan keseimbangan elektrolit dalam tubuh serta dehidrasi. pengobatan diabetes insipidus. berikut beberapa cara yang bisa dilakukan untuk mengatasi diabetes insipidus sentral: meningkatkan konsumsi cairan untuk mencegah dehidrasi. How you can tell the difference of diabetes insipidus vs siadh. diabetes insipidus: high urinary outputs, low levels of adh, high sodium levels, high serum osmolality, ongoing dehydration, and high levels of fluid loss. there may also be a genetic cause for this condition. siadh: low urinary outputs, high levels of adh, low sodium levels, low serum osmolality, being over-hydrated, and.
How are urine studies used to differentiate siadh from.
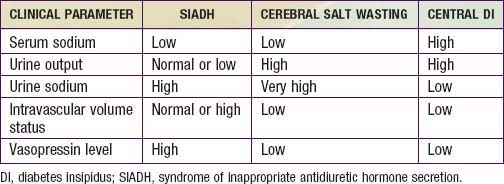
Treatment options for the most common types of diabetes insipidus include: central diabetes insipidus. if you have mild diabetes insipidus, you may only need to increase your water intake. if the condition is caused by an abnormality in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus (such as a tumor), your doctor will first treat the abnormality. Wu x, zhou x, gao l, et al. diagnosis and management of combined central diabetes insipidus and cerebral salt wasting syndrome after traumatic brain injury. world neurosurg. 2016 apr. 88:483-7. Secretion (siadh). however, cerebral salt wasting is a rare disorder that produces hyponatremia and can be difficult to distinguish from siadh. case report a 31-year old hispanic man with no past medical history presented after a fall with witnessed seizure and altered mental status. the patient was found to have a small subdural hematoma.
In contrast, a patient with diabetes insipidus has a plasma osmolality greater than 320 mosm/kg and a urine osmolality less than 100 mosm/kg. the ratio of urine to plasma osmolality is normally between 1. 0 and 3. 0. simultaneous determination of urine and plasma osmolality after three hours of water deprivation is useful in the differentiation. Siadh vs diabetes insipidus (di) for nursing endocrine system lecture exams and nclex review. this easy explanation on siadh vs di helps simplify the pathophysiology of diabetes insipidus and. Combined central diabetes insipidus and cerebral salt wasting syndrome is a rare clinical finding. however, when this happens, mortality is high due to delayed diagnosis and/or inadequate treatment. a 42-year-old white man was referred to neurosurgery. Combined central diabetes insipidus and cerebral salt wasting syndrome is a rare clinical finding. however, when this happens, mortality is high due to delayed diagnosis and/or inadequate treatment. a 42-year-old white man was referred to neurosurgery.
Comments
Post a Comment